RAM vs ROM

Computer memory has a lot of different features and attributes to remember that can confuse many. There are a few different types of memory that reside within your PC, different names for each, different purposes, variations, and much more.
Both RAM and ROM are two very different types of memory present in every PC. They have different purposes and actions to perform. In addition, both function in different ways and have many different features, making them both equally necessary for the proper function of any computer.
What’s the Difference Between Ram and Rom?
Here is all you need to know about the RAM vs ROM difference. This includes how both work, what they’re made of, and what makes each unique.
RAM
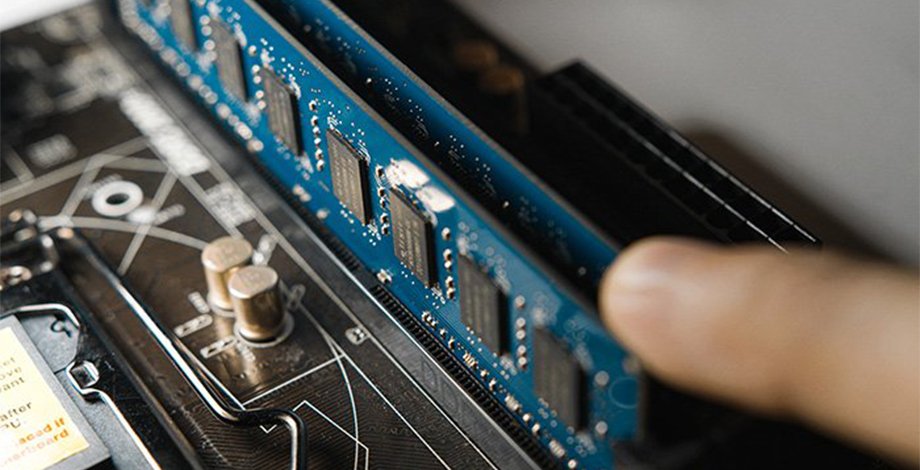
RAM stands for Random Access Memory. This is a PC component that sits on the motherboard in designated slots in the form of slim rectangle cards. They’re known as RAM sticks and differ in performance stats but not in size or shape regarding the actual slot.
RAM is classified as a volatile type of memory. This means that it’s not permanent, and is lost every single time the computer is shut down or restarted. That’s completely normal, as this type of memory isn’t designed to store permanent data like images, documents, or anything similar on your PC.
The main purpose of RAM is to store important pieces of data for various applications in order to reduce access time significantly. This allows each app on your device to load faster and provides the ability to load and run multiple apps simultaneously. It’s a very important component that has a part to play in determining the speed and performance of any PC. In addition, overclocking the RAM can boost speed given that the CPU can handle it.
If you ask yourself how much RAM your PC needs, the more the merrier is usually the answer. However, it has to match with other components like the CPU and motherboard to prevent you from going overboard.
ROM
Read-Only Memory, aka ROM, has a few significant differences compared to RAM. The main difference is that it is the opposite type of memory, a non-volatile one. This means that the data that gets written on this type of memory is there to stay, permanently.
As opposed to RAM, where data is stored as electricity and needs power not to be deleted, the memory in ROM is stored and written to each cell using binary code. This allows it to stay there even after there’s no more power to the computer. So even when you shut down the PC, everything that was stored on the ROM will still be waiting there when you turn it back on again.
ROM is also much slower when you compare it with RAM and features less storage capacity. The main way ROM is used in PCs is for the start-up process or bootstrapping, whereas RAM is used continuously while the computer is active. While ROM doesn’t affect your PC too much after start-up, RAM speed can have great effects on performance. This is why most users focus on getting gaming RAM.
Main Differences Between RAM vs ROM
Even though they are very different parts of the computer, both RAM and ROM deal with various types of memory and are crucial for a normally working PC. Here are the main differences that you need to remember when it comes to ROM vs RAM.
- It’s significantly faster to write data on RAM than it is on ROM
- RAM is volatile, whereas ROM is permanent
- RAM only holds power while there’s power. ROM can keep all the data even when power has been cut off and the PC is shut down
- ROM stores less data and has less storage capacity than RAM
- The main uses for RAM are in CPU cache and primary memory. The main uses for ROM are firmware and micro-controllers