Bone Conduction Tech. Everything You Need To Know

While regular headphones use tiny speakers to transfer the sound to your eardrums and later to the inner ear, there’s another way to perform the same task. Instead of playing sounds from speakers, bone conduction headphones use vibrations. Sounds interesting, right? But how exactly bone conduction tech works, where it’s used, and what about the sound quality? Find the answers to these questions below. Let’s start with the basics of bone conduction technology.
How Bone Conduction Technology Works
To understand bone conduction technology, we have to know how sound works. The gist of it is that sound waves are vibrations traveling through the air, or water, or some other medium. These vibrations have a variable amplitude (the higher the amplitude the louder the sound) and frequency.
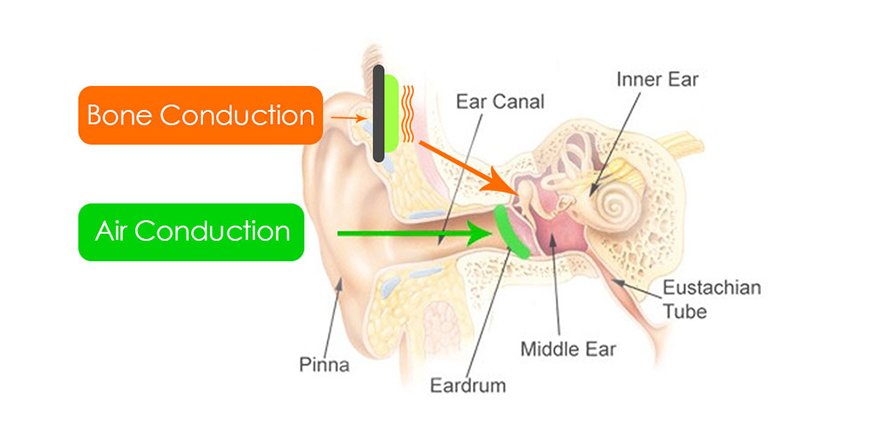
Differences Between Air and Bone Conduction – Image Source Wikipedia
Now, most of the sound we hear arrives through the eardrum, where sound waves are turned into physical vibrations. These vibrations are then picked by tiny bones of the middle ear. Finally, vibrations arrive in the inner ear and cochlea, inside which these vibrations turn into electric impulses. These nerve impulses are then transferred to the auditory nerve.
While the majority of sounds we hear are air-conducted and picked up by the eardrum, there are also bone-conducted sounds, such as our voice for instance. These sounds skip the eardrum and the middle ear and reach directly to the inner ear since they are traveling via bones of our head and jaw.
And this is the basis of the bone conduction technology. Instead of sending sounds to your ear the regular way, bone-conduction audio devices emit vibrations directly to the bones of our head, which are then interpreted by the cochlea like any other, regular sound.
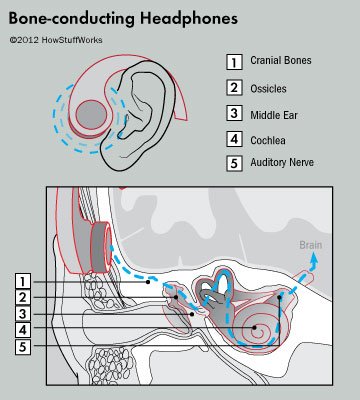
Differences In The Way Regular And Bone Conduction Headphones Deliver Sound – Image Source: howstuffworks.com
A pair of bone conduction headphones usually has two pads that reside on the user’s cheekbones or behind the ear. These speaker pads emit sounds in the form of vibrations, which are then picked up by the cheekbones and sent, via an arrangement of connected bones, to the inner ear where they are turned into nerve impulses.
Ludwig van Beethoven, the famous composer, is the most famous person who used bone conduction. Since Beethoven suffered from almost complete deafness, he wanted to find a way to hear his music again. And he found it. By clenching a rod with his teeth and then attaching the other end of the rod to a piano while playing it, Beethoven managed to perceive sound again because the vibrations from the piano traveled via the rod and his jaw to his inner ear, where they were interpreted as sound waves again.
But Beethoven wasn’t the first to use this technology. Mentions of the technology have been found in documents from the 16th century. Now, bone conduction tech wasn’t at the forefront of bleeding-edge innovation since then. Over the years headphones became and stayed by far the most popular way to listen to music (and other stuff) when on the go.
Bone Conduction Tech Applications
Since sounds transferred by our bones have much higher clarity than air-transferred sounds, bone conduction was used by divers, who were able to communicate via bone conduction headsets when underwater. Bone conduction headphones were also used in advertising campaigns and during musical performances.
One of the main markets for bone conduction technology is hearing aids. Hearing-impaired persons can use bone conduction hearing aids and headphones if their cochlea functions fine. Of course, another major field of usage is the military. Bone conduction tech not only produces sounds of high clarity, but it also leaves the ear and the eardrum unobstructed.
This allows soldiers to be completely aware of their surroundings and every sound around them, while at the same time being able to communicate with other soldiers and the HQ. As it usually happens, this once-military tech found its way to the consumer market, and today we have bone conduction headphones that can be purchased in the store near you.
Bone Conduction Headphones Vs Regular Headphones
Physical Design And Sound Isolation
As we’ve already explained, bone conduction headphones feature two vibration pads responsible for transmitting sounds. Regular headphones, on the other hand, have classic speakers. This makes the former much more limited in design.

A Pair Of Wireless Bone Conduction Headphones – Image Source: aftershokz.com
And since those pads have to have some kind of support in order to stay in one place, every pair of bone conduction headphones features a band going around the neck, providing support as well as housing batteries and other electronics. Most if not all current models are wireless without much differentiation in the form factor because of the inherent limitations of the technology. Some models also come with an optional microphone.
Regular headphones come in a variety of forms. You have wired as well as wireless models. There are over-ear, on-ear, and in-ear models, with lots of sub-variations like the over-ear open-back design, true wireless earphones, etc. And since each pair of regular headphones block the main source of sound perception, they can include stuff like active noise connection for improved sound isolation.
Bone conduction headphones do not block outside sounds. This makes them great for situations where you want to be aware of your surroundings (jogging, commuting, working in an open office environment) but still be able to listen to music or podcasts. On the flip side, lack of sound isolation makes these headphones a poor choice for environments with lots of background noise.
They also don’t have the tightest fit, which could make your jogging sessions a rather irritating experience. Finally, since they sit on your cheekbones or behind the ear, bone conduction headphones may induce fatigue over time.
Sound Quality
When it comes to sound quality, bone conduction headphones are noticeably behind regular models. This is not like the difference in sound quality between headphones and headsets; here, differences are much more pronounced.
One of the inherent issues with the bone conduction technology is that it transmits certain frequencies much better than the rest. This results in a hollow sound signature, with serious degradation of the sound quality. That’s not great for listening to music, but for stuff like podcasts and phone calls, bone conduction headphones are as good as regular ones.
Bone Conduction Headphones – When You Should Use Them
As we’ve already said, despite issues with fit and fatigue, these headphones are great for jogging, commuting, hiking, and all other activities where you want to be aware of your surroundings. And while they’re not great for music, high clarity makes bone conduction headphones excellent for podcasts and phone calls.
Other activities where these headphones can make a difference include swimming and snorkeling. Since the technology doesn’t use air-conducted sounds, you can use these headphones while swimming. The sound is super clear, and most models come with water resistance. This makes bone conduction headphones great for people who want to listen to some tunes or pods while getting wet.