What Is Ray Tracing and Should You Care?

In recent years, video games have been advertised with ray tracing, a technology which supposedly makes the gaming experience almost magical. Other than the obvious advertising campaigns launched with the release of the Nvidia 2000 series graphics cards in 2018.
However, ray tracing is a technology beyond one company’s marketing department, meant to enhance lighting in 3D rendered scenes.
Essentially, ray tracing is a way to make 3D scenes have realistic lighting, or as close to realistic as possible. There are many techniques that rely on ray tracing, but to understand it better, it would be wise to start with the very term.
What is Ray Tracing? – Understanding the Basics
By definition, ray tracing is a way of modeling light transport in algorithms for creating digital art, whether images or scenes. Ray tracing is less complicated when modeling a still image and much more so when scenes (like games) have to be rendered in real time.
Ray tracing was first deployed in pre-rendered scenarios, such as cutscenes, or more commonly, movies, as part of their visual effects. When it comes to real time rendering, even today, ray tracing hits the hardware so hard that the loss in performance is not only obvious, but in most cases, not worth the added flair.


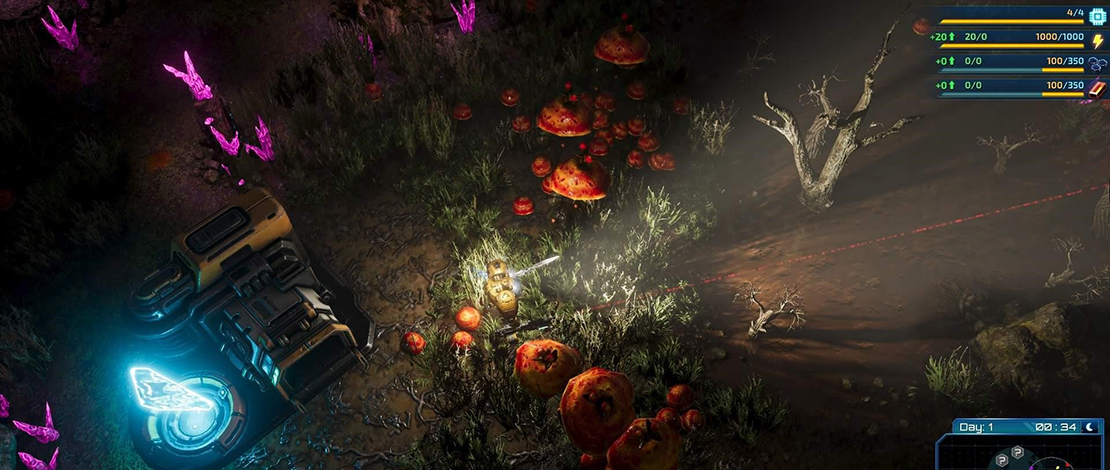
The bottom image is ray traced, showing respect for existing light sources in the scene, namely the building and the flashlight. This is a softer example of ray tracing, from the game The Riftbreaker.
How Old is Ray Tracing?
Ray tracing can be dated back to the 16th century and unlike many other origin stories, this one has an author, Albrecht Durer, a German artist, notably a painter. He theorized that you could project 3D images onto a two dimensional plane, which is what we do when we render scenes in games, using geometry.
He also pointed towards using rays as a reference as to what is visible and what should not be, which is how ray tracing works. Multiple techniques were described, but they weren’t used with computers until 1968.
It wasn’t until 1979 when Turner Whitted published a paper called “An improved illumination model for shaded display”, that the actual algorithms for ray tracing, the way we know it today, were presented to the world.
Even with that, ray tracing wasn’t used until the 2000s for movies, and it has only recently become available for video games, when graphics cards from Nvidia and AMD started using dedicated hardware accelerators for ray tracing.
Path Tracing – A Hungrier Ray Tracing Technique?
Regular ray tracing works by sending out rays of light from the camera/eye, which would bounce off objects, to be traced to the source/s of light. When the ray hits an object, a calculation is done to determine the object, or rather, pixel’s color.
Path tracing is different, because there are multiple rays sent for each pixel in the image. Often dozens or more rays are sent for each pixel in the scene, randomly. They are not sent back to the source after a single bounce, but rather as light would work in the real world.
Since path tracing causes noise which results in a very grainy image, multiple rays have to be traced in order for an image to look decent. And if you add that to a game which has moving parts and is rendered in real time, the performance hit is massive.
Path traced games are very rare and are often older titles such as Quake II, Return to Castle Wolfenstein and Portal. Even in those cases, only some parts of the illumination are path traced, such as global illumination, but not depth of field or motion blur.
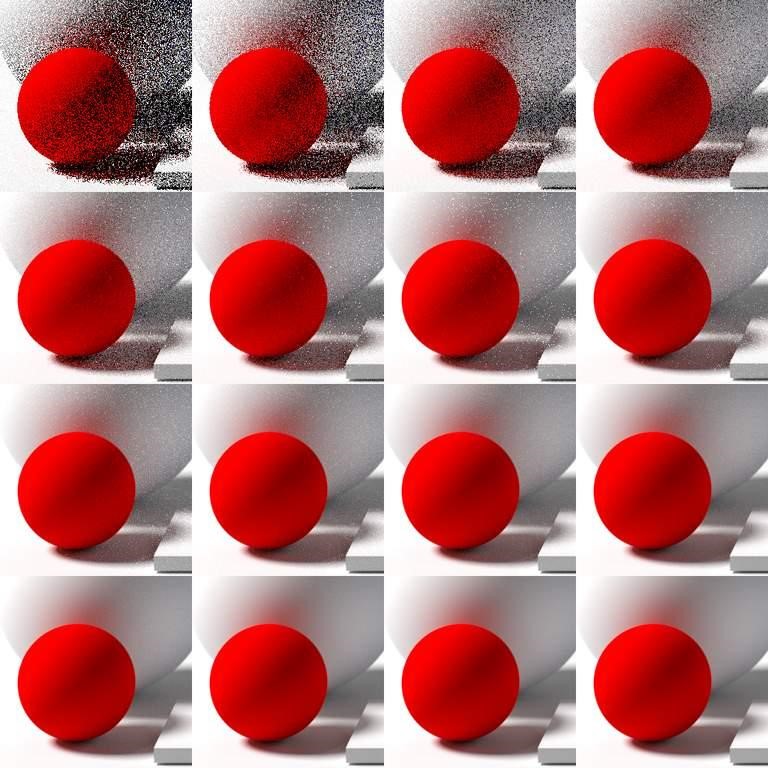
Starting from the top left with one ray per pixel, each subsequent image doubles in rays per pixel. This shows the noise and grain which is a side effect of too few rays when path tracing an image. Image source: Qutorial
What is Ray Tracing in Gaming?
For gamers, ray tracing is often not worth the performance loss. However, when implemented correctly, such as in Metro: Exodus, turning on ray tracing actually makes a worthwhile difference.
Essentially, ray tracing in games could make effects such as soft shadows, depth of field, dispersion, ambient occlusion, refraction, blur, reflections, and many more, better. That is not always the case, depending on the game engine and the time and effort the developers were allowed. It also depends on how much “fuel” the developers want to spend on ray tracing and which parts. Not all parts of illumination affect the scene in pleasing ways which would justify a lower frame time. What ray tracing should do is help make scenes in games as close as possible to how light works in the real world. When done right, reflections look as you would expect them, and even the simplest moments that don’t include any special or actionable gameplay, look amazing.
In other words, ray tracing really ups the immersion in any title, when you can actually tell the difference and not just by the performance deficit.
Even though the best graphics cards of today could sustain 60fps at 1080p, it is unlikely that someone spending over 1500$ on a graphics card is going to pair it with a 1080p monitor.
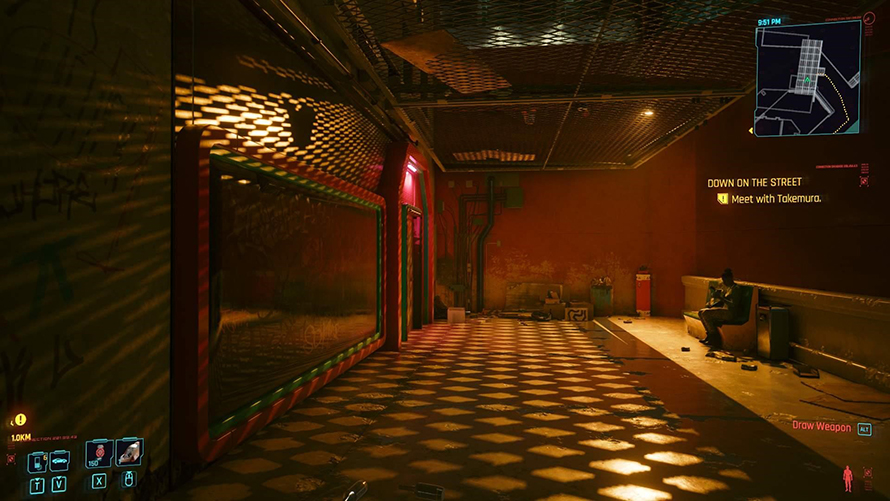


The bottom image has experimental path tracing on in Cyberpunk 2077.
Turning on path tracing with an AMD 6900 XT at 1080p ultra settings reduces the fps to 10 from 144. The game is not only not playable, but any moving object fails to render completely because of the GPU power used for the lighting math.
The lighting is much better and more realistic, but the game becomes literally unplayable.
How to Turn On Ray Tracing
All video games that have ray tracing require the use of either DirectX 12 or Vulkan as an API. Either the game will tell you when you try to turn ray tracing on in the settings, or you should manually launch the DirectX 12 executable of the game.
How to Turn Off Ray Tracing
Once you see your fps counter go down, you can turn the effect off the same way you turned it on, in the graphics settings of the game. It is either that, or upgrading your graphics card for the few titles that have decent ray tracing implementation.
Ray Tracing Is Great but Not Just There Yet
When you get around 80fps in a 20-year-old path traced game with one of the newest graphics cards on the market, you know that there is still work to be done on ray tracing for video games. Ray tracing is a way of rendering illumination in a scene, by tracing a ray to the light source, as it bounces off a surface. This technique can produce wonderfully realistic lighting, but at a performance cost.
If you are willing to sacrifice 50% or more of your performance for better lighting, then ray tracing should be ON in your games. It would be wise to check which game has good ray tracing prior to purchasing it.