CPU Socket. What Should You Know?
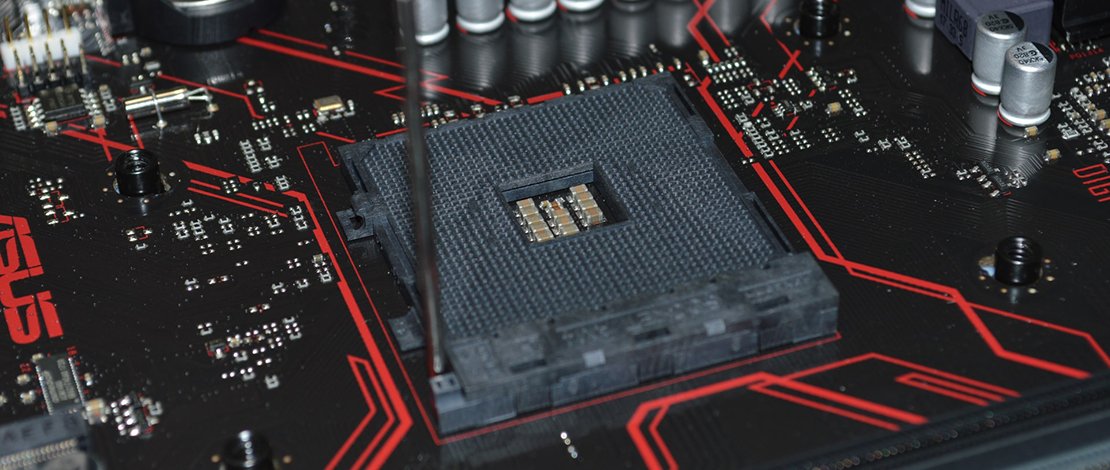

CPU socket is one of the most important parts of almost every motherboard. It’s a bridge between the CPU and the rest of the system and today, we’ll talk about CPU sockets in detail. Let’s start with explaining what the CPU socket is and why it’s so important.
What Is a CPU Socket?
A CPU socket is a housing for the CPU that connects it to the motherboard via an array of connectors in the form of pins. Via these pins, the CPU receives the power needed to function, as well as means to communicate with the rest of the system. On top of that, a CPU socket also contains a securing mechanism that keeps the CPU in place, preventing it from moving and thus potentially damaging itself or the board.
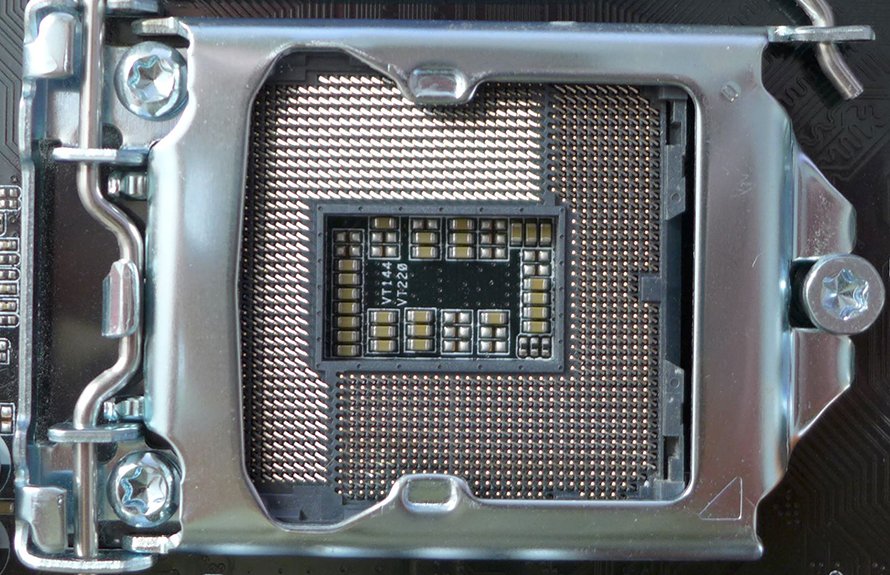

LGA 1151 Socket Used On Multiple Generations Of Intel CPUs
Now, there are many different CPU sockets out there. They are standardized in size, number of pins, and specs such as the maximum power delivery. Back in the day, a single CPU socket was made to house many different CPU generations. Some sockets even supported CPUs from different manufacturers. Nowadays, it’s rare to see a CPU socket made for more than two CPU generations. And, of course, there aren’t sockets that can house CPUs from multiple manufactures.
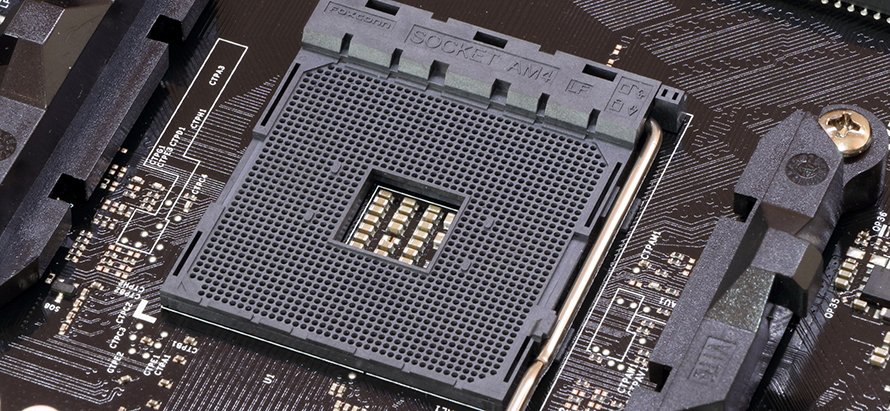
AMD AM4 CPU Socket
AMD’s AM4 socket is sort of an outlier when it comes to longevity since it debuted back in 2016 and was used for five (Excavator, Zen, Zen+, Zen 2, and Zen 3) CPU generations. That said, Excavator CPUs are incompatible with AM4 boards that support Zen CPUs, and vice versa.
Another important thing to know is that CPU coolers aren’t compatible with every CPU socket around. After you pick the CPU, look for a cooler that’s compatible with your CPU socket.
For instance, some popular air coolers that are on the market for a long time, like the Noctua NH-D15, didn’t support AM4 socket from the start. Noctua had to include a new mounting bracket for the AM4 socket to make the NH-D15 compatible with Ryzen CPUs.
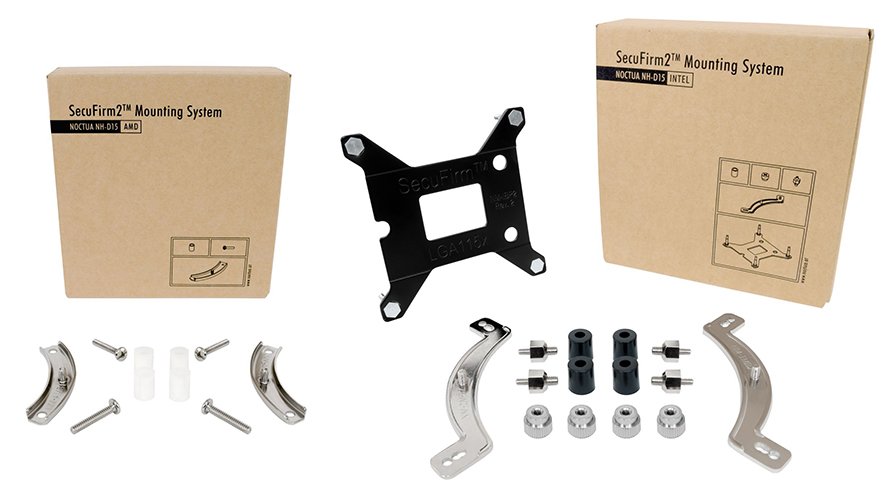

NH-D15’s AMD And Intel Mounting Mechanisms
So, to summarize. A CPU socket provides power to the CPU as well as ways for the CPU to communicate with the motherboard and the rest of the system. They differ in physical size, number of pins, and tech specs. You have different sockets for AMD and Intel CPUs. Further, nowadays a single CPU socket supports one or a couple of CPU generations, but there are outliers like the AMD’s AM4 socket. Now, let’s talk about different CPU socket types.
CPU Socket Types
There are two main types of CPU sockets in use today. LGA and PGA. The first is seen on every Intel CPU. LGA stands for “Land Grid Array.” This means that, when it comes to Intel CPUs, the pins are found on the socket, not on the CPU. AMD, on the other hand, uses a PGA or “pin grid array” socket for most of its CPUs. This means that, on a PGA socket, pins are found on the CPU.
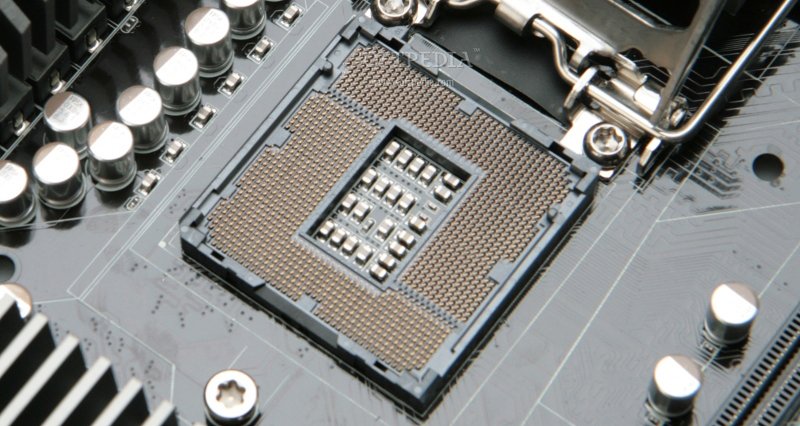


LGA Socket Next To LGA-Type CPU – Image Source: Softpedia; Overclock3d.net
While the PGA socket is used on most of its CPUs, AMD also uses an LGA-type socket for its Threadripper and EPYC lines of processors. Aside from reducing the chance to bend a pin (which is rather easy on a CPU die as large as EPYC or Threadripper that has thousands of connectors) while installing the CPU LGA sockets are also used because the installation procedure would’ve made a PGA socket extremely hard to install the CPU on.
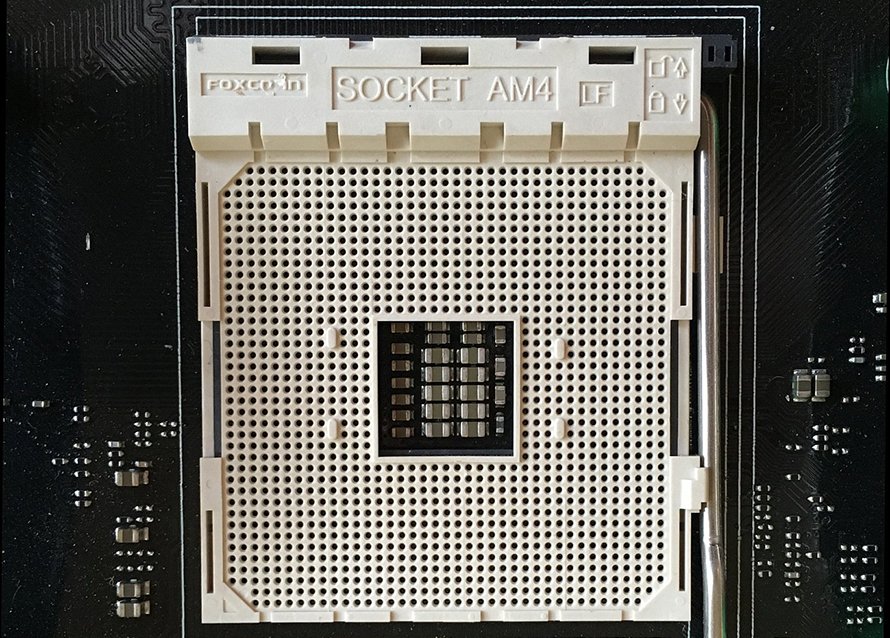

PGA Socket Next To A PGA-Type CPU – Image Source: hwsw; Quora
There’s also the third type of CPU socket called BGA. BGA stands for “ball grid array” and while technically a socket, ball stands for solder balls. In other words, the BGA socket requires a CPU to be soldered in order to connect to the board, making it impossible to replace or upgrade the CPU. BGA sockets are used in laptops and other devices where a CPU is soldered to the motherboard.
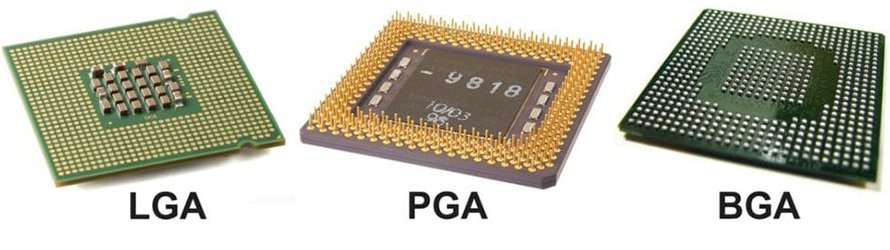
Differences Between LGA, PGA, and BGA CPUs – Image Source: Hellotech
Now, as we’ve already explained, if a CPU uses the LGA technology and the CPU socket is also LGA that doesn’t mean they are compatible. The same goes for PGA sockets. There’s a ton of different CPU sockets, with the most important differentiating factor being the number of the pins. But, in some cases even if both the socket and the CPU use the same socket and the same number of pins, they aren’t compatible.
This happened with the LGA1151 socket from Intel. While the socket stayed the same all the way from the 6th to the 9th gen CPU lineup, 7th, and 8th gen CPUs didn’t work on boards made for 6th and 7th gen CPUs, and vice versa. On the flip side, there are adapters that can make CPUs work on sockets they aren’t officially compatible with. In any case, when you decide to get a new gaming CPU, pick the CPU first and then start looking for the motherboard with a compatible socket, not the other way around.
You need to buy an AMD EPYC processor and turn it over. There are no pins. My suggestion is a bit better understanding of this topic would be in order before posting in the future.