What is Dynamic QoS and Should You Care?

What does Dynamic QoS do exactly?
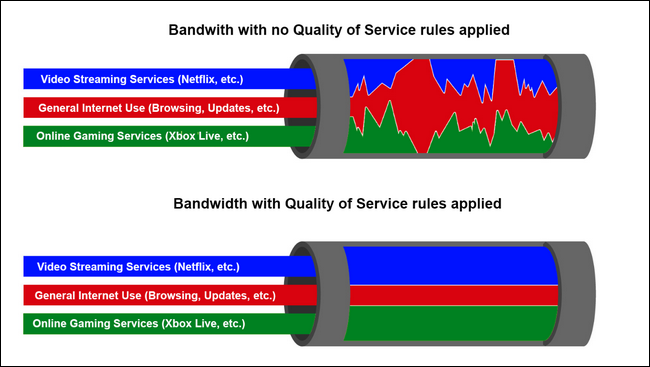
Quality of service (QoS) is an excellent tool that enables you to manually distribute bandwidth traffic on your router and optimize your internet for activities like gaming and streaming.
The traffic of your gaming and streaming applications can be sent first, which will improve performance.
Source: howtogeek
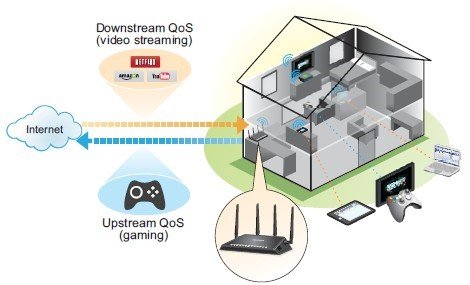
Dynamic QoS lets you distribute network traffic between applications like your browser and your local devices such as your PS5. This can help to minimize lag during online gaming, but also let you distribute bandwidth equally for the devices connected to the router.
Source: Netgear
QoS is also a good optimization tool for general internet users.
Say if someone is downloading a large file, whether dynamic QoS is on or off will determine how the bandwidth will be distributed. If QoS is off, he will get the first come first serve option on which all routers function, so no internet will be left for the rest of the devices connected to that router, but if QoS is ON he will get a portion of the internet provided, therefore leaving enough for other devices to function.
Networks with a Quality of Service model applied will prioritize certain applications, services, and/or users over others so the important things (Netflix, Skype calls, your Xbox Live connect, etc.) have the most bandwidth and the best ping time.
Should I enable Dynamic QoS?
If your Internet download and upload speed is 250 Mbps or less then you can benefit from enabling Dynamic QoS.
If you use a gigabit Internet connection (300 Mbps or faster), then you don’t need to use QoS.
Did you get gigabit connection but you still use an old router that doesn’t support 150+ mbps? Find your fix with these best routers under 100$.
Dynamic QoS can be extremely effective for a SD-WAN, it completely changes how networks are monitored and managed.
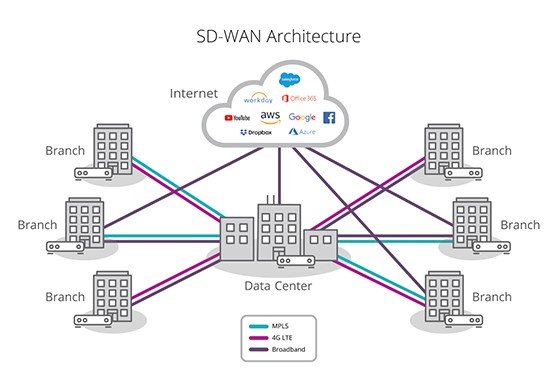
It changes from reactive to proactive, from manual to automated and as a natural consequence it changes your network from costly to cost-effective, both in terms of deployment and operations.
A network dark-out in your business network, with the help of dynamic QoS, can now be converted into a non-emergency maintenance ticket. Better yet, if the black-out can be fully mitigated, all the associated cost of this network emergency can be 100% avoided. Continued access to your cloud services means zero downtime and happy end-users as well as happy managers.
If you have the responsibility for a business network that covers a wide space you should check out some routers for long range connections.
How to enable dynamic QoS?
The following tutorial is for NETGEAR routers, so make sure you grab one if you want to follow these steps.
Note that this guide is general directions as the settings listed here look different on every router.
Here’s how to enable Dynamic QoS on a NETGEAR router:
- Launch a web browser from a computer or phone device that is connected to the network.
- Type http://www.routerlogin.net or http://www.routerlogin.com. A login screen displays.
- Enter the router user name and password. The user name is admin. The default password is password. The user name and password are case-sensitive. The BASIC Home screen displays.
- Select Dynamic QoS.
- Select the Enable Dynamic QoS check box.
- Specify your Internet bandwidth. You must specify your Internet bandwidth so that Dynamic QoS can perform bandwidth allocation and traffic prioritization. To allow Speedtest to detect your Internet bandwidth (recommended): For more accurate Speedtest results, make sure that no other devices are accessing the Internet.
- Click the Apply button. Your settings are saved. A link displays on the bottom of the screen to view bandwidth utilization. Clicking the link displays the Attached Devices screen where you can manually distribute bandwidth between devices.
While you’re in the settings you may want to take a look at these security settings that everyone should change but no one does.
How to manually distribute bandwidth between applications (Games, Netflix etc.)?
The above setting will optimize your traffic automatically but you can follow this guide for manual distribution. (Note: only experienced users recommended).
- Type http://www.routerlogin.net or http://www.routerlogin.com. A login screen displays.
- Enter the router user name and password. The username is admin. The default password is password. The user name and password are case-sensitive. If you need assistance with router login, see How do I login to my NETGEAR home router?. NETGEAR genie displays.
- Click ADVANCED > Setup > QoS Setup.
- Click Upstream QoS > Setup QoS rule. The QoS Priority Rule list displays.
- To add a priority rule, scroll down to the bottom of the QoS Setup screen and click Add Priority Rule.
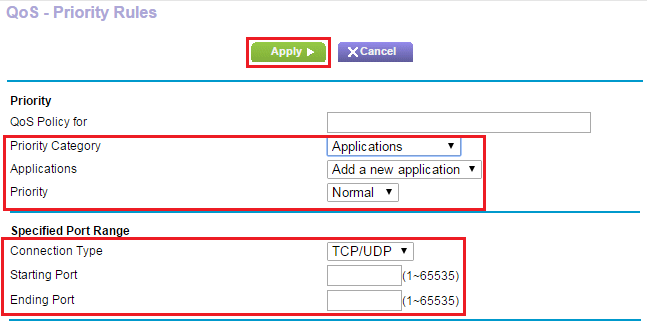
- In the Priority Category list, select either Applications or Online Gaming.
- Select Add a new application, or Add a new game, as applicable.
- If prompted, in the Connection Type list, select either TCP, UDP, or TCP/UDP.
- Specify the Starting Port number and Ending Port number that the application or game uses.
- From the Priority list, select the priority for internet access for this traffic relative to other applications and traffic. The options are Low, Normal, High, and Highest.
- Click Apply.
Source: Netgear
The rule is saved.
Note that if you are unexperienced with wifi settings you might get problems like those that some users report:
“The quality of service option is supposed to help prioritize network traffic, but in actuality, it often slows down important connections, misidentifies devices and cripples upload speeds. While it can theoretically do some good on very crowded networks, QoS can also create more problems than it solves.”
The service means well, but it just doesn’t seem that good at prioritizing traffic. One user complained of QoS routinely prioritizing a Linux PC dead last in his network; others noted that wireless data always seems to get priority over wired. Gaming and streaming applications almost always seem to take priority over uploading productivity files, which can obviously be a problem for users who need their home networks for both work and entertainment.