How to Recover Unallocated Space on USB Drive?
USB drives are susceptible to various read/write errors, mostly because they are removable drives and are often exchanged between many computers. These computers may have different operating systems which might not always do things the same, which can lead to write errors, or in some cases, read errors on another PC.
The effect of such errors, not to mention possible viruses, are typically missing partitions or drive space. Unallocated space on a USB drive can easily be fixed, or rather, recovered, through a couple of simple steps.
It is important to understand what might cause these errors, to avoid them in future use.
USB Drive Showing Less Space
Flash drives are media that typically change file system formats more often than any other drive. Typically, your hard drive or SSD has a single format and it is usually either NTFS, ext4, btrfs, APFS if you’re using Apple computers.
Since drives travel from one computer to another, they encounter different approaches to copying and pasting files, not to mention formatting. There is also the problem with user consistency. Not all users dismount flash drives before removing them, which is the best practice when handling any type of drives.
Here are a couple of common reasons why USB drives lose space:
Bootable Drives
A flash drive’s file format can change with every single format, particularly if you’re not careful what you select.
Creating bootable flash drives changes the file system, depending on the system that is copied to the drive. More often than not, every bootable flash drive has at least two partitions, one which holds the bootloader and another which holds the rest of the information.
Upon the next format, both partitions of the drive might not get deleted, just the one with the bootloader, leaving you with unallocated space and a very small partition.
Viruses
Viruses were once a more common reason as to why flash drives would malfunction. Today, even though there is still malicious code online, the antivirus tools are also better. On most systems, however, people don’t even use antivirus tools, given that browsing practices have also become better.
It is good to check your computer for malware every once in a while. Any antivirus tool should have an antimalware tool as well, including all the free ones.
Forgetting to Unmount the Drive
Typically, you can remove the drive before unmounting it, but it is not a good idea to do so. This is more of a problem for Windows users, who neglect the “Safely Remove Hardware” icon. All drives first need to be mounted in order to be used.
Linux users know this and most unused drives, internal drives included, are connected but not mounted. Make sure to hit the “Safely Remove Hardware” button on Windows, and do the same on any other system.
Interrupting Copying or Formatting
This is a big no in any type of action. Canceling an operation such as copying is okay, but canceling formatting can be more dangerous. The last thing that you should do in situations like these is forcibly removing the drive if an operation seems to be stuck.
That could lead to a write error and a loss of space.
Failed Formatting
Sometimes, when a drive needs formatting, the process may fail. There are applications that might simply get things wrong, which might not be their fault, actually. If any of the previous errors happened, the application might just format a single partition instead of the entire drive. This can happen after making a bootable drive.
How to Reclaim USB Drive Space
USB drives, or flash drives, are relatively easy to work with when it comes to space recovery. Depending on the system that you are using, there are applications which can help you do the job without opening a terminal or console.
Let us look at fixing unallocated space in the three most common operating system types, Windows, Linux and macOS.
Windows
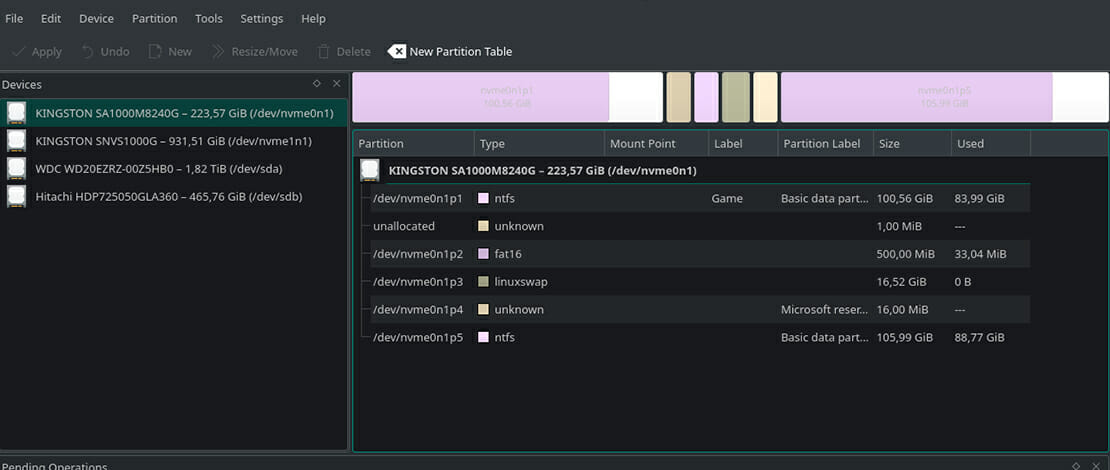
When using Windows, the easiest way to deal with unallocated space is to use their own Disk Management utility. It can be opened by typing its name in the start menu, which will then search for the program in question.
Once you open the application, you will be met with the following window. It will display the information about the drives and their partitions as such. You can see a list and another, simpler representation in the separate window below.
Note that in the image, the partitions in the red rectangle cannot be read by Windows, even though they are detected. The partitions, in this case, are ext4 and belong to a Linux distribution.
Microsoft has a decent guide on how to extend drives that have unallocated space. Unallocated space is marked black, while used space is blue.
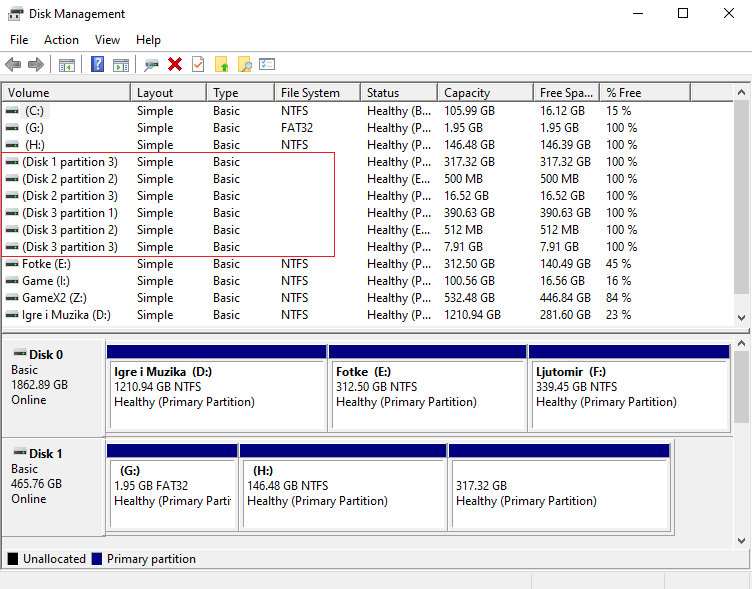
Linux
Linux has a graphical utility called GParted, which uses GNU Parted, or is rather the graphical front-end for the said application. This is great for Linux users who do not want to use the terminal.
Note that various Linux distributions may have their own utility, although GParted should work just fine on any Linux distribution. Take note that GParted is the official utility for the GNOME desktop environment, but regardless offers great support and help.
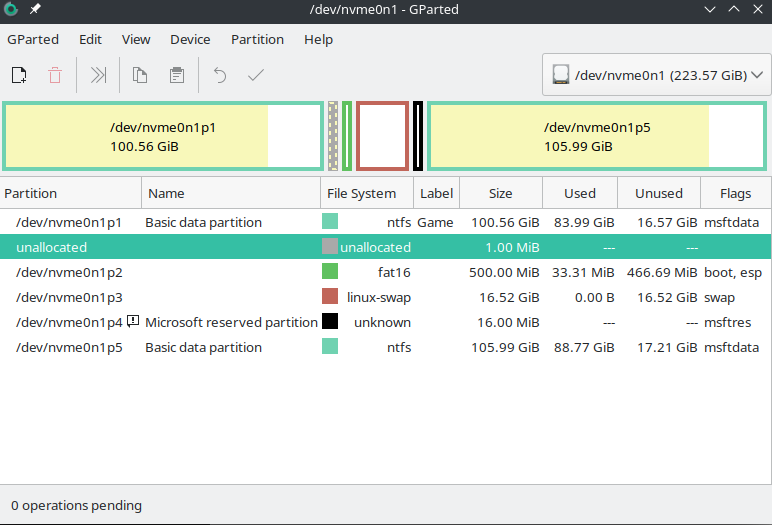
The interface is similar to most other partition management utilities. Linux uses a different naming format, for example, in this image you see an NVME drive and its many partitions.
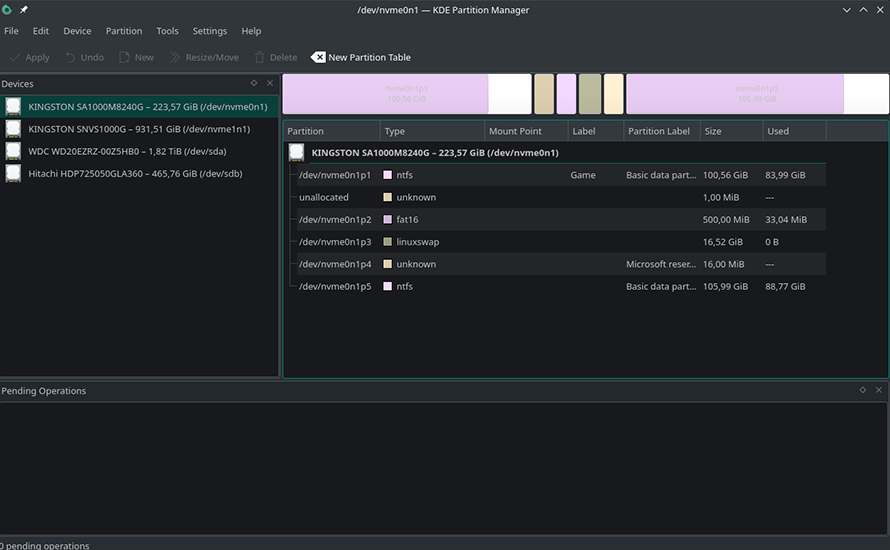
On the KDE desktop environment, you have KDE Partition Manager as the official tool, though others like GParted will also work just fine. This tool shows the drives on the left and the partitions on the right.
macOS
Macs have their official utility called Disk Utility. You can search the Dock for it or open it manually. The utility is simple and offers a pie chart representation of your drives. Make sure to select the right drive before formatting. Apple has a great guide on how to use Disk Utility.
Conclusion and Summary
Whenever your USB drive has unallocated space, make sure to diagnose why it happened, by following the tips you have here. No matter whether you use the best flash drive or a cheap one, unallocated space errors typically have to do with either mistakes made by the user or a software error when formatting a drive.
Each operating system, fortunately, has official applications to help solve these common issues, Disk Management, GParted and Disk Utility, for Windows, Linux and macOS, respectively.